How to Calculate Revenue Potential of a New Start-up and Present to Investors
A start-up’s current revenues are a good predictor of their future revenue potential. Unlike one-time deals or one-off services rendered to clients, recurring revenue — such as revenue derived from subscriptions — are especially interesting to investors and lenders. This is because they can point to sticky future income streams and are a baseline for future revenue growth.
What SaaS Metrics Demonstrate Revenue Potential?
You need have some indicators that show your business is healthy and growing for potential investors, employees and other partners.
Investors and lenders will not only want to review your financial reporting, they’ll want to see how your company is performing based on key SaaS metrics.
These SaaS metrics include:
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
- Committed Monthly Recurring Revenue (CMRR)
- Average Revenue per Customer (ARPC)
Investors use this data — MMR, CMRR, and ARPC — to see if your company is a good investment.
What is Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)?
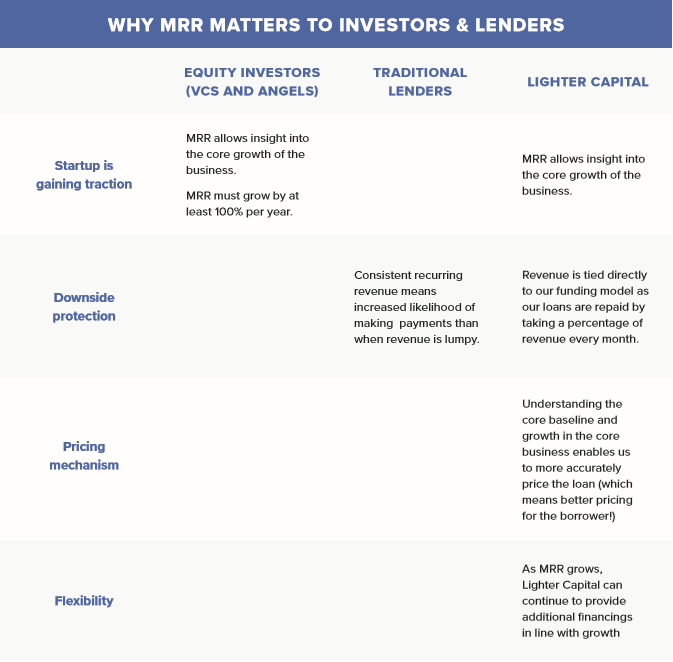
Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) measures the monthly amount of total revenue that’s subscription-based or recurring in nature and highly likely to continue into the future. This number excludes all one-time, non-recurring payments, such as implementation or professional service fees, hardware, and discounts.
On an annualized basis, this metric is known as Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR).
The formula to calculate monthly recurring revenue is:
MRR = (Average monthly subscription value per customer) × (Number of customers)
As a key indicator for growth, measuring your MRR on a month-over-month basis is critical for understanding whether you’re gaining traction or starting to stall.
For financial planning purposes, MRR is particularly helpful since it’s relatively stable and predictable. Once you have a history of tracking your MRR, you can use it to model out estimates of where you’ll be in the coming months and can plan your business accordingly.
However, remember that MRR does not represent your actual cash flow. If you’re receiving all of your money upfront, you’ll still be incurring costs to service that contract over the rest of its term, without receiving any additional cash inflow.
What is Committed Monthly Recurring Revenue (CMRR)?
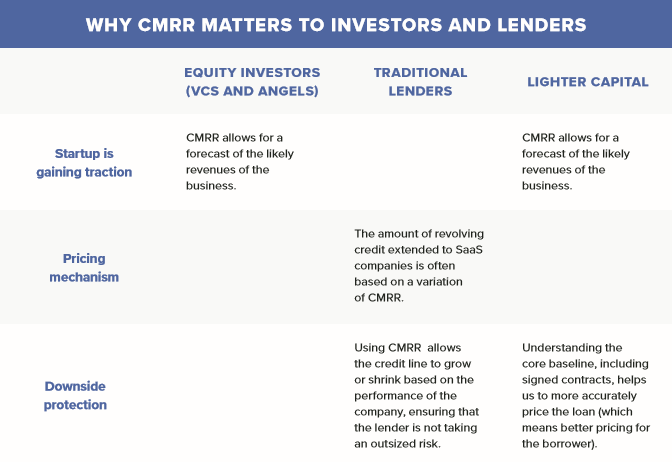
Committed Monthly Recurring Revenue (CMRR) looks at current MRR, as defined as (New Business + Expansion – Contraction – Churn), and then adds in signed contracts going into production and subtracts out revenue that’s likely to churn within that period.
The terms included in the definition of CMRR are defined as:
- New Business MRR: MRR associated with leads that convert to paid customers in a given time period.
- Expansion MRR: Any increases in MRR from existing customers in a given time period. These could be the result of customers adding additional subscriptions, upgrading, etc.
- Contraction MRR: Any decreases in MRR from existing customers in a given time period. These could be the result of downgrading to a lower plan, adding or increasing a discount, etc.
- MRR Churn: MRR from customers who cancel or fail to renew their subscription in a given period.
The formula to calculate committed monthly recurring revenue is:
CMRR = MRR + Signed Contracts – Expected Churn
Unlike MRR, which only yields insight into the current run rate of a company, CMRR incorporates potential future changes. Committed monthly recurring revenue provides a forecast for the company’s performance, based on what you know about your customers today.
Knowing your CMRR and how it’s trending over time can enable you to more accurately forecast revenues and provides a better picture of the financial standing of the company.
What is Average Revenue per Customer (ARPC)?
Average Revenue per Customer (ARPC) is the average revenue generated from each customer per month (or per year). Sometimes the metric can be further broken down by customer segment or product type, such as the ARPC for enterprise-level customers, or the ARPC for Product A.
The formula to calculate average revenue per customer is:
ARPC = Total Revenue / Customer Count
Knowing the ARPC of your different SaaS products or services will help you identify up-sell opportunities. A good business practice is to monitor the change in the ARPC over time.
You can get the ARPC of your products and services from your accounting software or from third-party software.

Keep Track of These Metrics
Along with all other key SaaS metrics, there is no one industry definition for measurement. As you begin to track these metrics, be sure to document how you’re calculating them — and remain consistent over time. Having thorough documentation will make it easier when you have to present these metrics to potential investors and lenders.
Source: https://www.lightercapital.com/blog/how-to-calculate-revenue-potential/